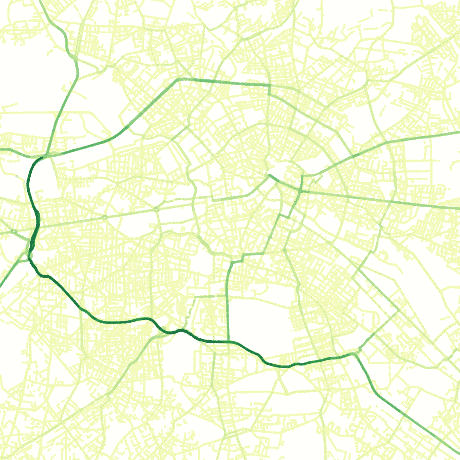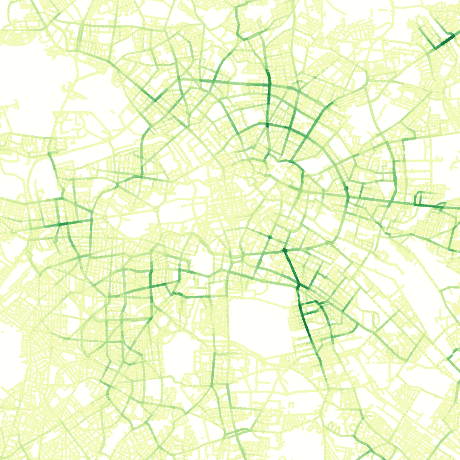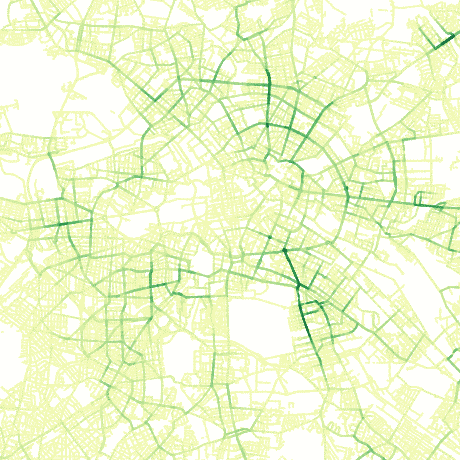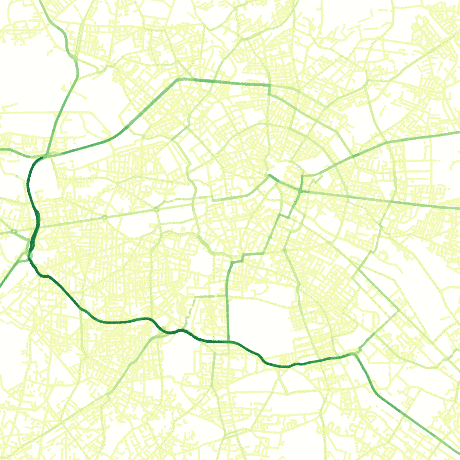
Estimate average daily traffic on a road network by sampling a distribution of shortest paths.
To compile this project you'll need an installation of Rust. It's recommended to install the latest stable release using rustup.
During runtime you'll also need an installation of the OSRM backend that serves as the routing engine.
See here for more details.
- Install dependencies
sudo apt install build-essential git cmake pkg-config \
libbz2-dev libxml2-dev libzip-dev libboost-all-dev \
lua5.2 liblua5.2-dev libtbb-dev- Compile
git clone https://github.com/Project-OSRM/osrm-backend/
cd osrm-backend
mkdir build
cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
cmake --build .- Install
sudo cmake --build . --target install- Construct routing graph for area of interest
Geofabrik provides OpenStreetMap extracts for different regions as *.osm.pbf files
(https://download.geofabrik.de/).
These can be used by OSRM to build a routing graph.
# Download OSM extract
wget http://download.geofabrik.de/europe/germany/berlin-latest.osm.pbf
# Build routing graph
osrm-extract -p /usr/local/share/osrm/profiles/car.lua berlin-latest.osm.pbf
osrm-partition berlin-latest.osrm
osrm-customize berlin-latest.osrm- Start OSRM backend server
osrm-routed --algorithm mld berlin-latest.osrm-
Install Rust (stable) with rustup.
-
Compile
git clone https://github.com/b-r-u/nori
cd nori
cargo build --release- Run this project
(Make sure the OSRM backend server is running and you have created an *.osrm file)
cargo run --release -- sample -n 1000 --osrm berlin-latest.osrm \
--geojson berlin.geojson --routes berlin.routes --png berlin.png \
--uniform2d --bounds 52.4422 13.2392 52.5738 13.5125 --max-dist 5000
# See all command line options
cargo run --release -- -h- Ensure a specific distribution of trip lengths, either log-normal or given by a histogram
- Simplify the network's geometry, map edges to a ground truth and compare traffic values