You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: Bubble Sort/README.markdown
+114-1
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
1
1
# Bubble Sort
2
2
3
-
Bubble sort is a sorting algorithm that is implemented by starting in the beginning of the array and swapping the first two elements only if the first element is greater than the second element. This comparison is then moved onto the next pair and so on and so forth. This is done until the array is completely sorted. The smaller items slowly “bubble” up to the beginning of the array.
3
+
Bubble sort is a sorting algorithm that is implemented by starting in the beginning of the array and swapping the first two elements only if the first element is greater than the second element. This comparison is then moved onto the next pair and so on and so forth. This is done until the array is completely sorted. The smaller items slowly “bubble” up to the beginning of the array. Sometimes this algorithm is refered as Sinking sort, due to the larger, or heavier elements sinking to the end of the array.
4
4
5
5
##### Runtime:
6
6
- Average: O(N^2)
@@ -12,3 +12,116 @@ Bubble sort is a sorting algorithm that is implemented by starting in the beginn
12
12
### Implementation:
13
13
14
14
The implementation will not be shown as the average and worst runtimes show that this is a very inefficient algorithm. However, having a grasp of the concept will help you understand the basics of simple sorting algorithms.
15
+
16
+
Bubble sort is a very simple sorting algorithm, it consists in comparing pairs of adjacent elements in the array, if the first element is larger, swap them, otherwise, you do nothing and go for the next comparison.
17
+
This is accomplished by looking through the array `n` times, `n` being the amount of elements in the array.
18
+
19
+
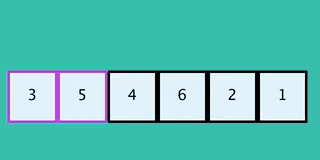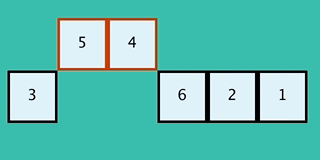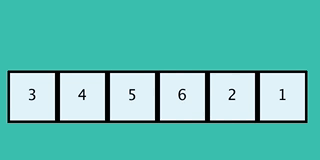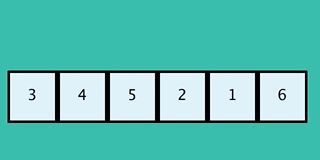
20
+
21
+
This GIF shows a inverted implementation than
22
+
23
+
#### Example
24
+
Let us take the array `[5, 1, 4, 2, 8]`, and sort the array from lowest number to greatest number using bubble sort. In each step, elements written in bold are being compared. Three passes will be required.
25
+
26
+
##### First Pass
27
+
[**5 1** 4 2 8 ] -> [**1 5** 4 2 8 ], Here, algorithm compares the first two elements, and swaps since 5 > 1.
Now, the array is already sorted, but the algorithm does not know if it is completed. The algorithm needs one whole pass without any swap to know it is sorted.
44
+
45
+
##### Third Pass
46
+
[**1 2** 4 5 8 ] -> [**1 2** 4 5 8 ]
47
+
48
+
[ 1 **2 4** 5 8 ] -> [ 1 **2 4** 5 8 ]
49
+
50
+
[ 1 2 **4 5** 8 ] -> [ 1 2 **4 5** 8 ]
51
+
52
+
[ 1 2 4 **5 8**] -> [ 1 2 4 **5 8**]
53
+
54
+
This is the same for the forth and fifth passes.
55
+
56
+
#### Code
57
+
```swift
58
+
for i in0..<array.count {
59
+
for j in1..<array.count {
60
+
if array[j] < array[i] {
61
+
let tmp = array[i]
62
+
array[i] = array[j]
63
+
array[j] = tmp
64
+
}
65
+
}
66
+
}
67
+
return array
68
+
```
69
+
70
+
#### Optimization
71
+
The bubble sort algorithm can be easily optimized by observing that the `n-th` pass finds the `n-th` largest element and puts it into its final place. So, the inner loop can avoid looking at the last `n-1` items when running for the `n-th` time:
72
+
73
+
```swift
74
+
for i in0..<array.count {
75
+
for j in1..<array.count- i {
76
+
if array[j] < array[i] {
77
+
let tmp = array[i]
78
+
array[i] = array[j]
79
+
array[j] = tmp
80
+
}
81
+
}
82
+
}
83
+
return array
84
+
```
85
+
86
+
The only change made was on the second line, changing the interval from `1..<array.count` to `1..<array.count - i`, effectively cutting the number of comparisons by half.
87
+
88
+
The ordering with the optimized code would look something like this for the array `[5, 1, 4, 2, 8]`:
[ 1 2 **4 5** 8 ] -> [ 1 2 **4 5** 8 ], As the first loop has occured once, the inner loop stops here, not comparing 5 with 8
107
+
108
+
##### Third Pass
109
+
[**1 2** 4 5 8 ] -> [**1 2** 4 5 8 ]
110
+
111
+
[ 1 **2 4** 5 8 ] -> [ 1 **2 4** 5 8 ] again, stoping one comparison short
112
+
113
+
##### Fourth Pass
114
+
[**1 2** 4 5 8 ] -> [**1 2** 4 5 8 ]
115
+
116
+
There is no Fifth pass
117
+
118
+
#### Conclusion
119
+
120
+
Even with the proposed optimizations, this is still a terribly inefficient sorting algorithm. A good alternative is [Merge Sort](), that not only is better performing, has a similar degree of dificulty to implement.
121
+
122
+
*Updated for the Swift Algorithm Club by Julio Brazil*
0 commit comments