 +
+
+
+  +
+
+
+  +
+
+
+ uv run -m newton.examples cable_bend
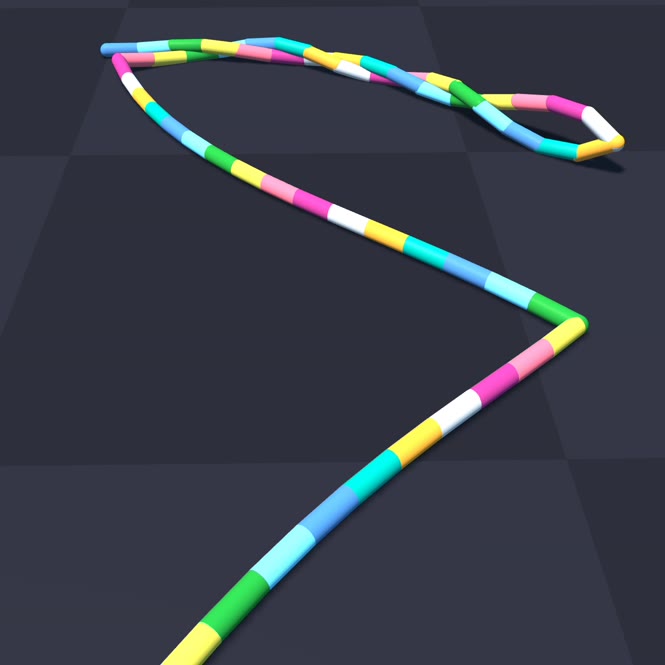
+ uv run -m newton.examples cable_twist
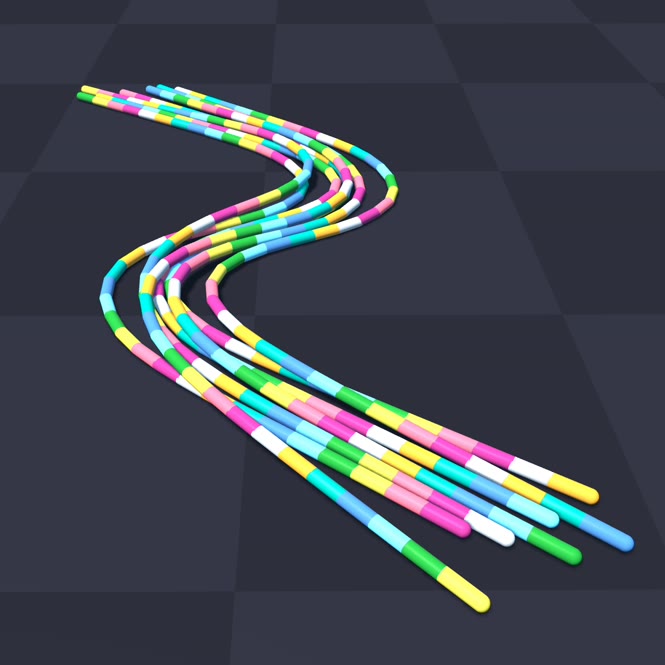
+ uv run -m newton.examples cable_bundle_hysteresis
+
+
+  +
+
+
+ |
+
+
+  +
+
+
+ |
+
+
+  +
+
+
+ |
+
+ uv run -m newton.examples cable_bend
+ |
+
+ uv run -m newton.examples cable_twist
+ |
+
+ uv run -m newton.examples cable_bundle_hysteresis
+ |
+