🎵 Download your recently played Spotify tracks data
This Python project automates the process of retrieving and storing recently played tracks from Spotify. It integrates with the Spotify API to fetch data, including track details, artist information, and playback timestamps. The data is then cleaned, processed, and saved into a CSV file, ensuring that no duplicate entries are stored. Additionally, the project includes a feature to insert the collected data into a PostgreSQL database, facilitating further analysis or integration with other systems. This solution is ideal for music enthusiasts and developers looking to maintain a personal log of their Spotify listening history or integrate it into larger applications.
git clone https://github.com/Sissaz/spotifyCreate a new .env file in the cloned project 'src' folder with all the lines below, replacing only CLIENT_ID and CLIENT_SECRET
CLIENT_ID=YOUR_CLIENT_ID
CLIENT_SECRET=YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET
REDIRECT_URI=http://localhost:8888/callback
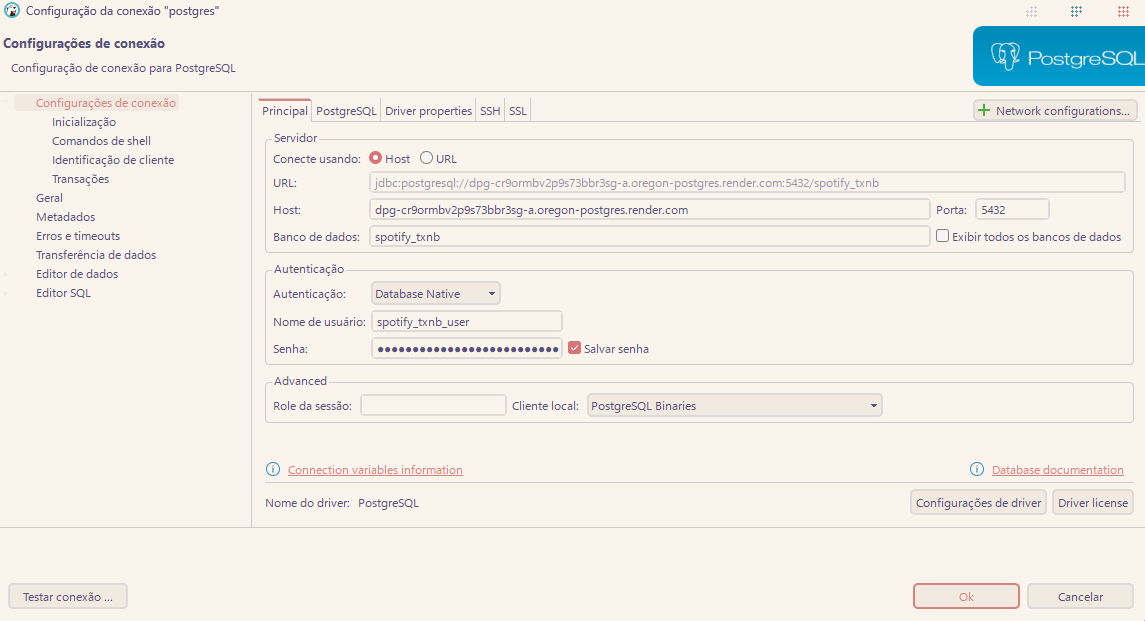
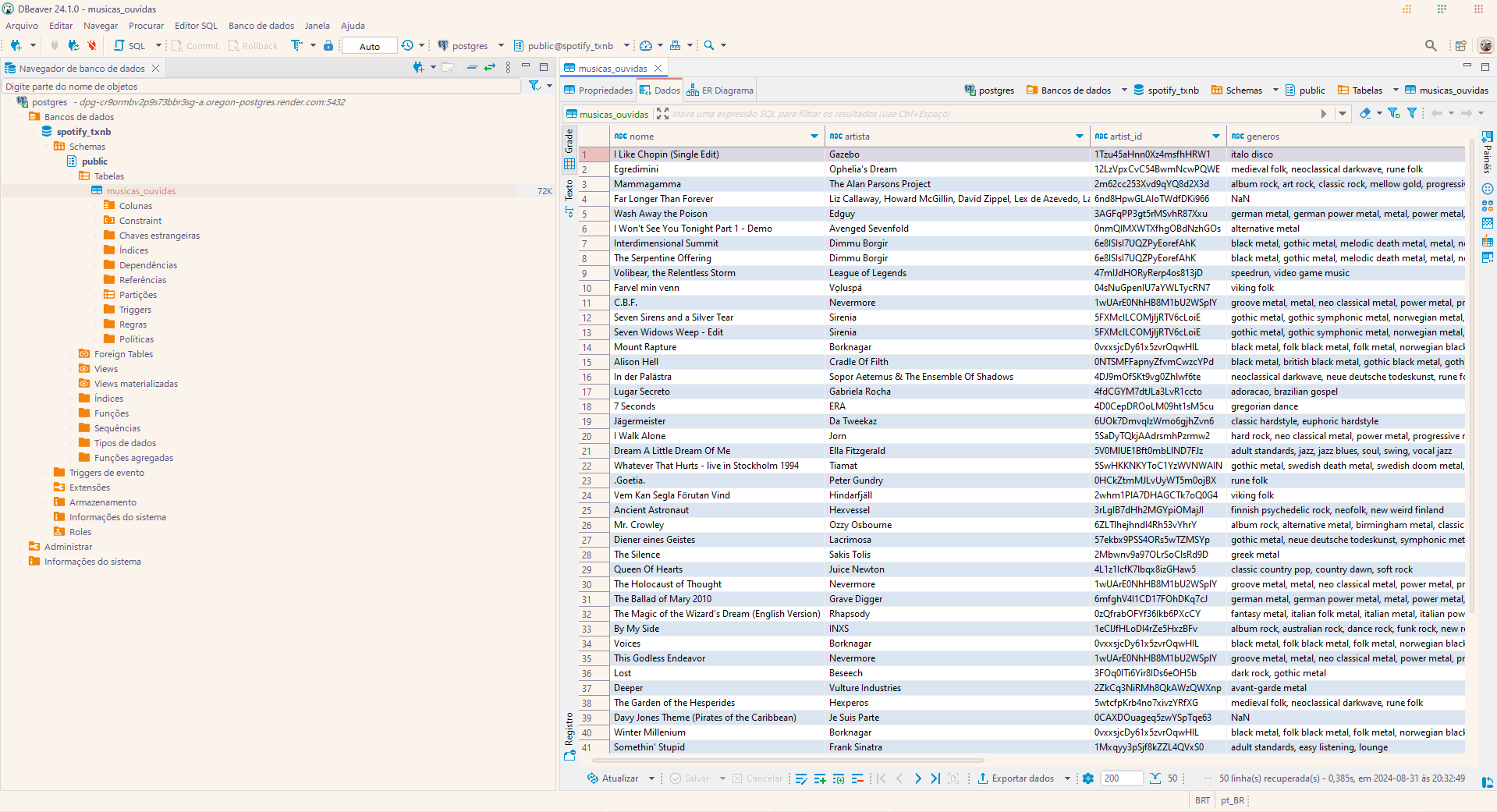
REFRESH_TOKEN=pip install poetrycd srcpoetry env use 3.12.1poetry installcd assetspoetry shellpoetry run python musicas_recentes.pyThis example demonstrates connecting to a PostgreSQL database using DBeaver. The connection was made possible through a free PostgreSQL instance provided by Render, which offers 1GB of capacity and is available for up to one month, allowing seamless interaction with the database.
Python Code: Download your recently played Spotify tracks data
...
def escrever_csv(musicas, output_filepath):
df = pd.DataFrame(musicas) # Converte a lista de músicas em um DataFrame
# Verifica se o arquivo já existe
if os.path.isfile(output_filepath):
# Carrega o CSV existente
df_existente = pd.read_csv(output_filepath)
# Concatena as novas linhas com as existentes, adicionando as novas linhas no topo
df_final = pd.concat([df, df_existente], ignore_index=True)
else:
# Se o arquivo não existir, apenas use as novas linhas
df_final = df
# Remove duplicatas com base em todas as colunas
df_final.drop_duplicates(inplace=True)
# Salva o DataFrame final no arquivo CSV, mantendo o cabeçalho
df_final.to_csv(output_filepath, index=False, encoding='utf-8')
print(f"Arquivo CSV atualizado com novas linhas no topo e duplicatas removidas. Salvo em {output_filepath}")
...