version number: 1.0.7 author: Arnour Sabino
A python library to measure algorithms execution time and compare with its theoretical complexity.
To install use pip:
$ pip install almetro
Or clone the repo:
$ git clone https://github.com/arnour/almetro.git
$ python setup.py install
Almetro uses timeit module from python to time your algorithms.
See more here
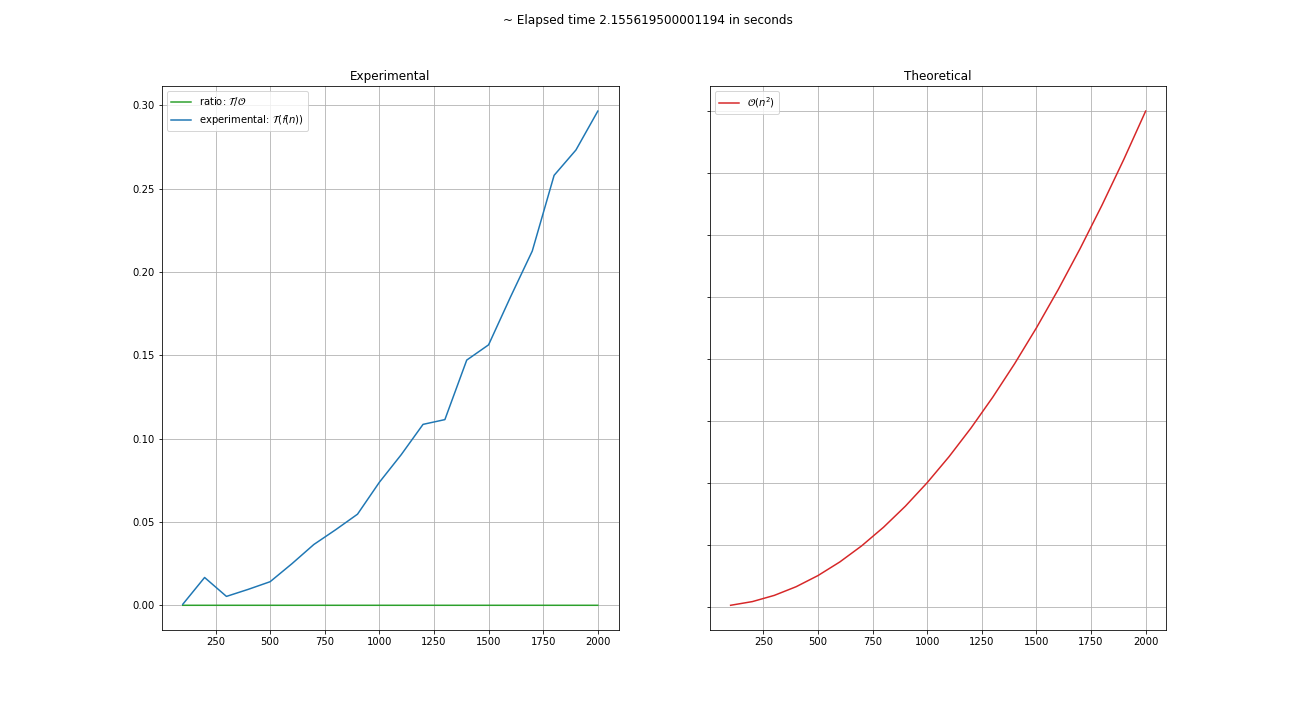
Applying Almetro to a quadratic algorithm:
import almetro
from almetro.algorithms import loop_n_quadratic
from almetro.complexity import cn_quadratic
from almetro.instance import growing
metro = almetro\
.new()\
.with_execution(trials=5)\
.with_instances(instances=20, provider=growing(initial_size=100, growth_size=100))\
.metro(algorithm=loop_n_quadratic, complexity=cn_quadratic)
chart = metro.chart()
chart.show()Applying Almetro to a lg n algorithm:
import almetro
from almetro.algorithms import loop_n_log
from almetro.complexity import clog_n
from almetro.instance import growing
metro = almetro\
.new()\
.with_execution(trials=100)\
.with_instances(instances=20, provider=growing(initial_size=10000, growth_size=10000))\
.metro(algorithm=loop_n_log, complexity=clog_n)
chart = metro.chart()
chart.show()Customazing execution:
import almetro
from almetro.complexity import Complexity
from almetro.instance import generator
my_custom_complexity = Complexity(
theoretical=lambda v=1, e=1, c=1: v * v,
experimental=lambda v=1, e=1, c=1: v + e,
text='O(v^2)',
latex=r'$\mathcal{O}(v^2)$'
)
# You need to provide instances as dict: {'name': '', 'size': {}, 'value': {}}
# Size must contains all needed theoretical complexity arguments
# Value must contain all needed algorithms arguments
def my_custom_instances(n):
g = create_some_graph()
for _ in range(n):
yield {
'name': 'my instance name',
'size': {'v': len(g.nodes()), 'e': len(g.edges())}, 'c': some_order_value(),
'value': {
'graph': g,
'v': len(g.nodes())
}
}
def my_custom_algorithm(graph, v):
# Do some stuff
pass
N = 50
instances_generator = my_custom_instances(N)
# Trials determine how many times each instance will be repeated for Almetro to pick the min time. That way you can exclude some noise from your analisys.
metro = almetro\
.new()\
.with_execution(trials=5)\
.with_instances(instances=N, provider=generator(instances_generator)\
.metro(algorithm=my_custom_algorithm, complexity=my_custom_complexity)
metro.chart().show()metro.table().show()