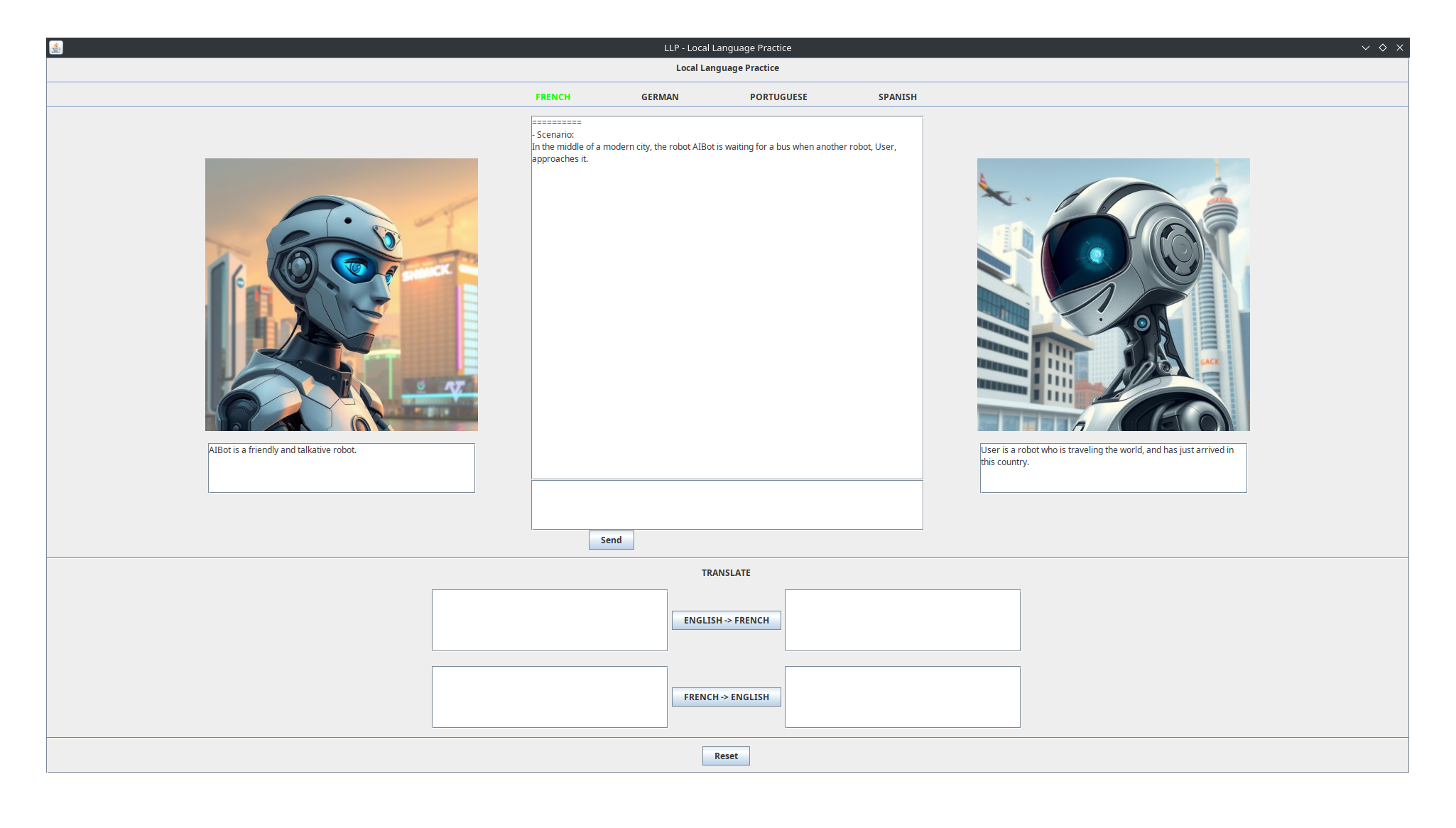
Local Language Practice (LLP) is a desktop application to practice languages through chatting with a local LLM.
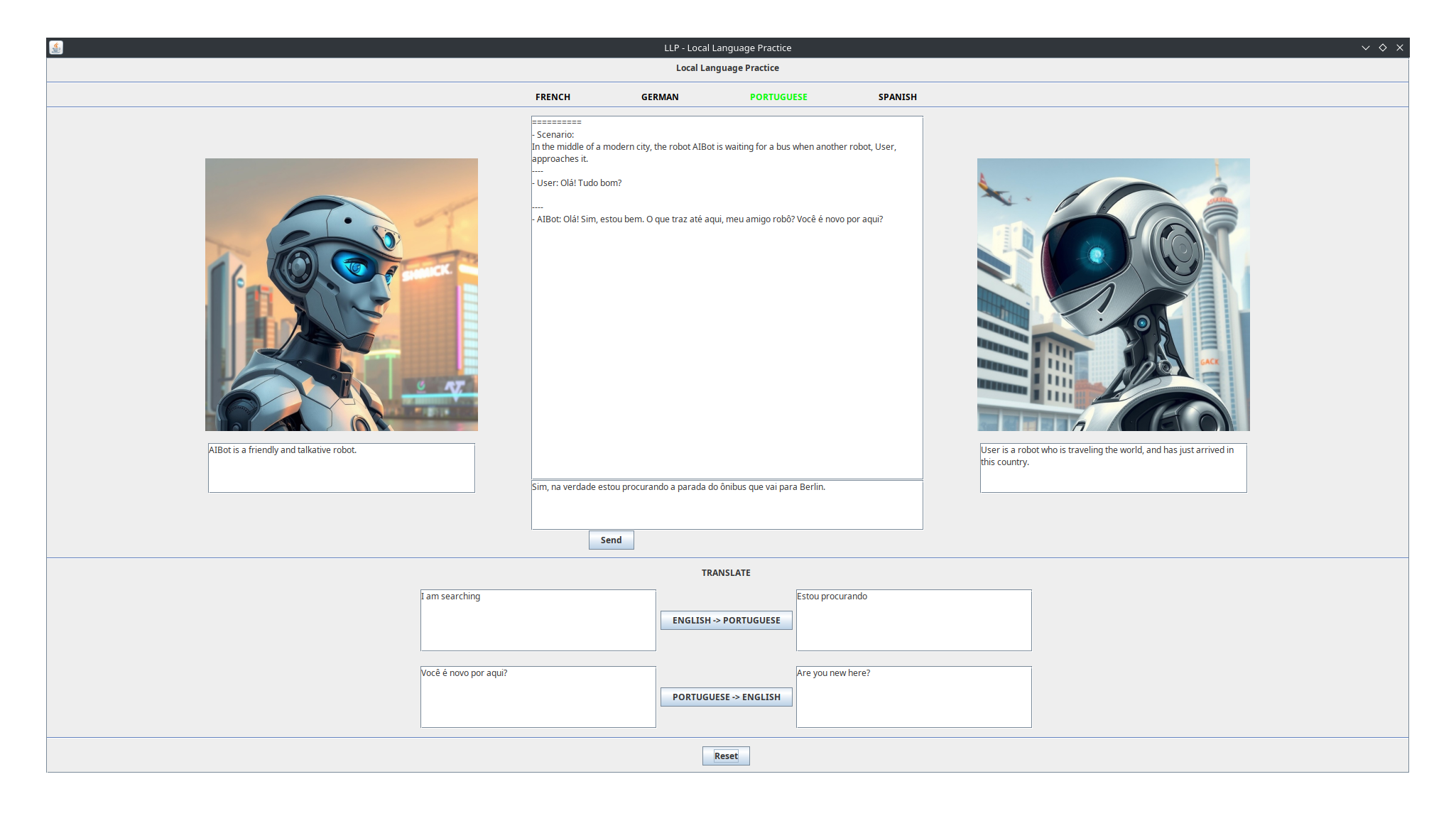
The application allows you to chat as a fictional character with another fictional character, played by an AI model. When starting it, you can see the description of the scenario and of each character, as well as the character avatars, in the main view. At each turn of the conversation, just type in your next message in the language you want to practice, and the AI will answer to it in the same language.
If you are not sure how to write something in the language you are practicing, or if you do not understand something that the AI wrote, you can use the widgets below the main chat to translate any text between English and the language being practiced, in either direction. Use this as you chat to clarify and enhance your understanding of the language without having to switch from the application into a dictionary or translation app.
You can change the language being practiced by selecting a different one from the list of supported languages on the top of the main view.
The application assumes you have an LLM API listening on port 8080 of your computer (port number is configurable, check section below). If you have experience configuring and running them, any with an OpenAI-compatible API should work nicely - if you do not have experience, the easiest way to get one running is to use llamafile, which is both easy to use and has very good documentation on how to set it up.
Don't like the results you have been getting? Just try another model! Llamafile's documentation explains how to use a single executable to run different models, the same should be true for any other tool you might choose.
The application is written in Java, so you will need to have the Java runtime installed. Assuming it has already been installed, either download the Jar file from the latest entry in the Releases section of this repository or build the project following the instructions below, and execute it.
Example with llm server running on default port (8080):
$ java -jar LLP.jar
Example using a custom port (8888, in this case):
$ java -jar LLP.jar -p 8888
If you are using ollama for the LLM server, you will have to at a minimum pass the name of the model you want to chat with when starting the application by using the -m <model_name> option. You will probably also want to use ollama's default port, 11434. Here is an example of how to chat with llama3.1 using ollama (check ollama's documentation for other model options):
$ java -jar LLP.jar -p 11434 -m llama3.1
Keep in mind that ollama will use an incredibly small context size, regardless of the model you are using. In order to have a larger context size, you will need to create a custom version of the model, specifying the size to be used - this might be a somewhat more advanced configuration that you should try only after you feel comfortable with ollama. Please refer to its documentation for steps on how to set the context size for the model when using the OpenAI-like API (which LLP does).
Here is the list of command-line options available when starting the application:
-
-p <port_number>: Set the port where to reach the LLM server, <port_number> must be an integer indicating a port in your machine with a LLM server listening. Defaults to 8080. -
-m <model_name>: Specify the name of the LLM model to be used, <model_name> must be a string. Necessary when using ollama as backend for text generation, has no effect when using llamafile. -
-t <temperature>: Specify the temperature to be used when generating text, the larger the temperature the more randomness it includes. must be a decimal number, and usually fits in the [0.0-1.0) range. Make sure to use a dot (.) and not a comma to separate the parts of the number. Defaults to 0.9.
These options are independent of each other, and can be combined as desired and in any order. Examples of using some of them can be found in section "How to run" of readme.
Although it is not possible to edit the practiced scene in the application itself, it is possible to load different scenes from a file in order to practice whichever scenario one wants. For this, you will need to create a .practice file in JSON format - you can use the file samples/default_session/default.practice as a reference for the required fields. Once you have created a custom .practice field with all the fields correctly filled, just import it through the respective button in the UI of the application.
This is a simple Maven project, so the easiest way to build it is running mvn clean package in the LLP folder (assuming Maven is installed - if not, check its site and install from there). A jar file containing everything the application needs to run will be created at LLP/target/LLP-<VERSION>.jar.