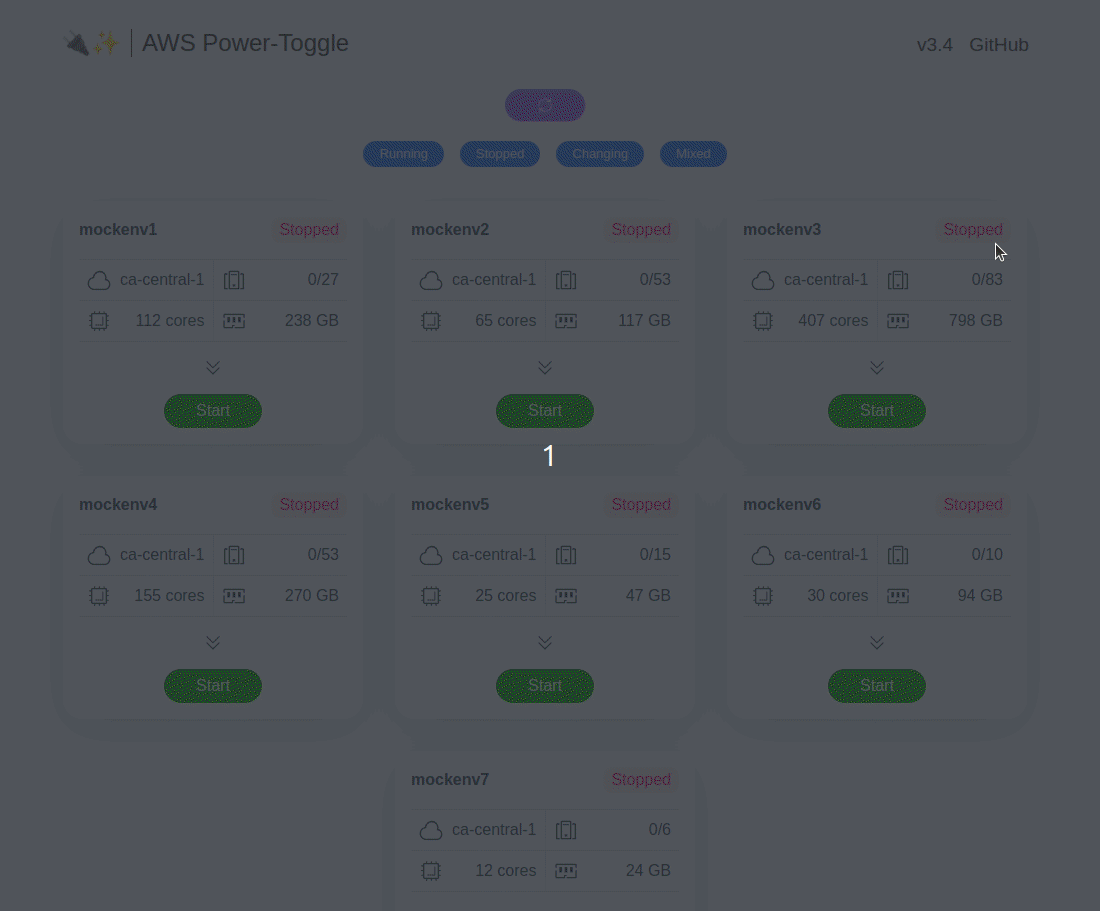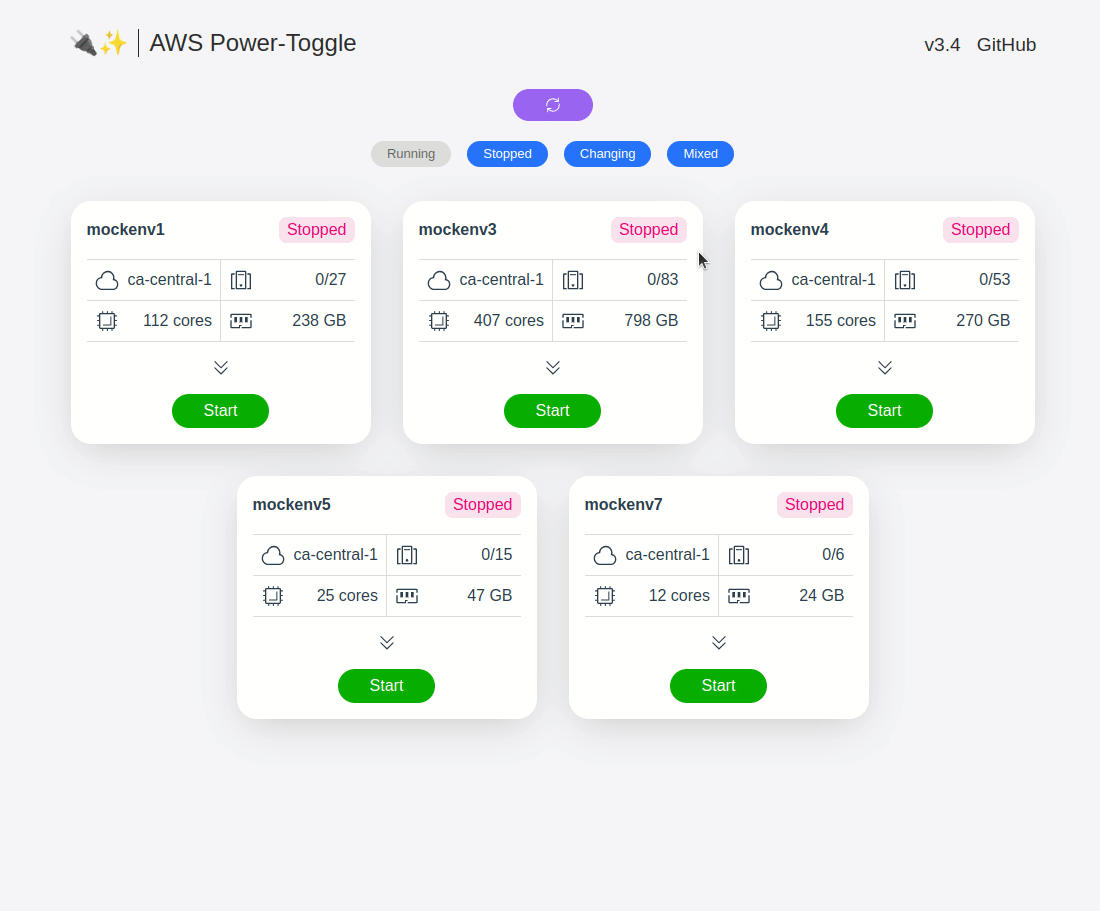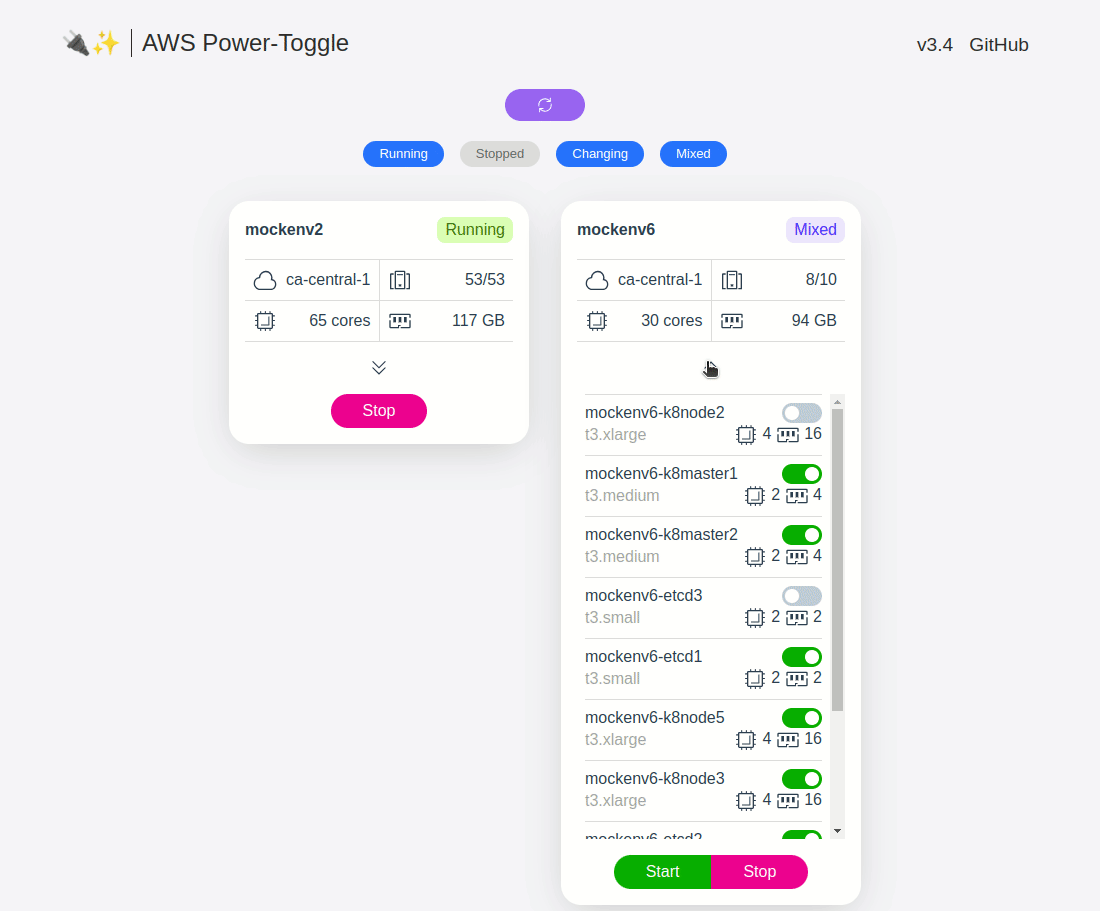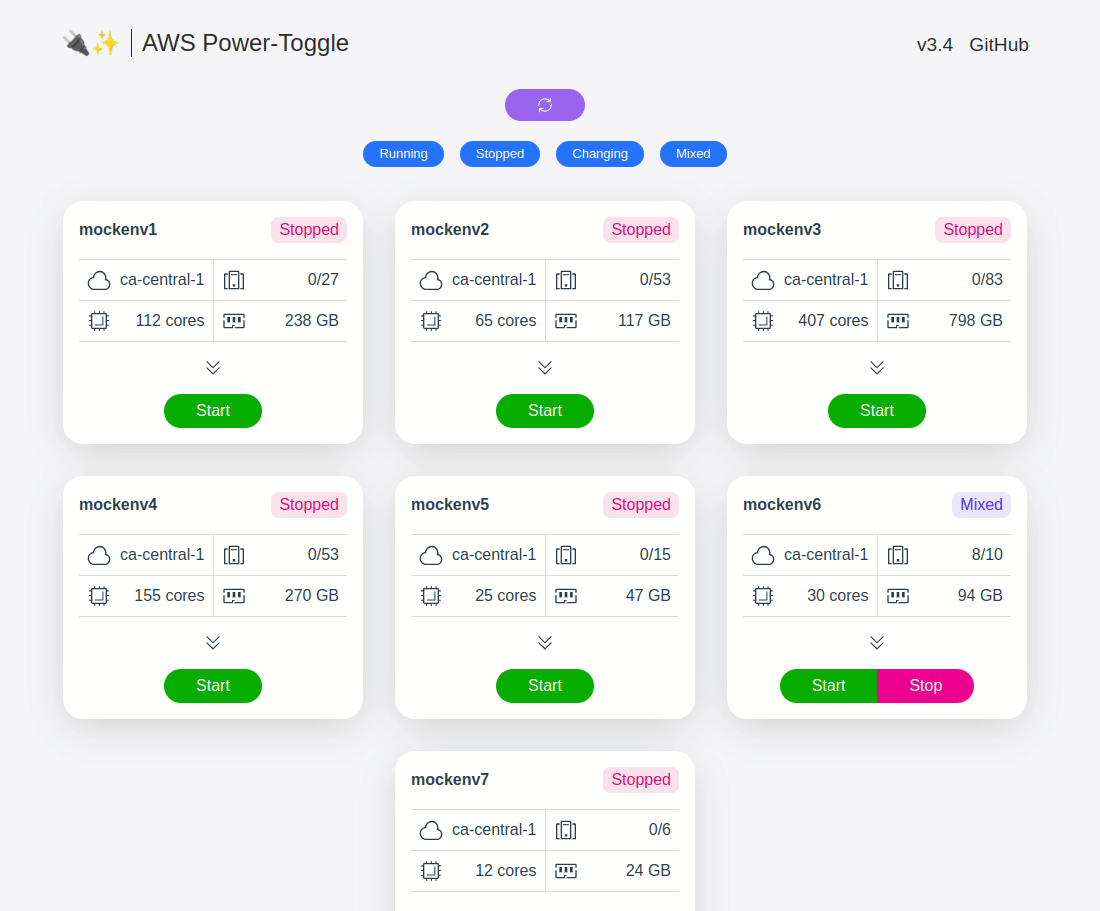
web UI and API for quickly starting and stopping AWS environments. See gif below or visit the demo site to check it out.
aws-power-toggle groups your instances by environments (via instance tag described below), then allows you power toggle them with a single action. This can be very useful when you have to deal with a ton of developers who have multiple environments and need to use them sporadically. While you could leave them on all the time, it may result in your boss(es) freaking out about the bill :) Just hand this web UI and/or API to the devs and let them decide when to start/stop the environment(s). Don't forget to check up on them to make sure they are actually turning them down when not in use :)
The backend polls the aws API periodically (or on demand through web ui). In order for your instances to show up the following
instance tags are required (all other instances are ignored):
power-toggle-enabledset totrueEnvironmentset to non-empty value
Both the tags listed above are configurable via the config file (see power-toggle-config.yaml).
Instances are grouped by the value of Environment tag. Please note that tag values are *case-sensitive.
the backend requires an API key to successfully poll AWS (shock). Once you have obtained it, set the following environment variables:AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
Once you have tagged your AWS instances appropriately (hopefully with terraform or the aws cli) then your ready to deploy. Ofcourse, this is done quickest via docker:
docker run -d --name "aws-power-toggle" \
-p 8080:8080 \
-e "AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<your_key_id>" \
-e "AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=<your_secret_key>" \
gbolo/aws-power-toggle:3.4
Then open your browser to: http://127.0.0.1:8080
Enabling support for ASGs can be done via the config file or setting the environment variable POWER_TOGGLE_AWS_ENABLE_ASG_SUPPORT=true.
In order for them to be discovered they MUST have the required tags) applied directly on the ASG (the instance tags are ignored).
The ASG will show up as a single toggleable instance for associated environment, with the cpu/memory being the cumulative total of all instances associated with that particular ASG.
NOTICE: when the above conditions are met, power-toggle will be able to interact with your ASGs in the following manner:
- When an ASG is toggled off, BOTH the minimum and desired capacity will be set to 0
- When an ASG is toggled on, BOTH the minimum and desired capacity will be set to 1
The backend server API is written in go and the frontend web UI is written in javascript (vue.js).
The backend also serves the frontend content, so the frontend must be built prior compiling the backend.
By far, the easiest way to build this project is to use docker:
make docker
this will build the docker image, which builds both the frontend and backend.
The supported version of nodejs is defined in the .nvmrc file located in the root of this repo. We use nvm to easily switch to this version (but nvm is NOT a requirement):
# switch to supported nodejs version (if using nvm)
nvm install
# build the frontend
make frontend
this should create the static web root directory located in ./frontend/dist/
The backend should be buildable with versions of go v1.8 or greater.
make backend
this should create a binary located in ./bin/aws-power-toggle
Once built, you can run it like:
# edit the config if needed: ./testdata/sampleconfig/power-toggle-config.yaml
# make your changes to source code or config then export your aws api key
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<your_key_id>
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=<your_secret_key>
# run it
./bin/aws-power-toggle -config testdata/sampleconfig/power-toggle-config.yaml
# do a test API call
curl -v 127.0.0.1:8080/api/v1/env/summary
$ make help
all Build both backend and frontend
backend Build backend binary
docker Build docker image
frontend Build frontend
dep Run dep ensure to fetch dependencies
fmt Run gofmt on all source files
goimports Run goimports on backend source files
lint Run golint
test Run go unit tests
clean Cleanup everything
For further details on an API endpoint (including example responses), click on the endpoint's name.
-
EnvAllSummary:
GET /api/v1/env/summaryretrieves a summary of all known environments -
EnvSummary:
GET /api/v1/env/{env-id}/summaryretrieves a summary of a single environment -
EnvAllDetails:
GET /api/v1/env/detailsretrieves full details of all known environments (including list of instances) -
EnvDetails:
GET /api/v1/env/{env-id}/detailsretrieves full details of a single environment (including list of instances) -
StopEnv:
POST /api/v1/env/{env-id}/stoptriggers a shutdown of an environment -
StartEnv:
POST /api/v1/env/{env-id}/starttriggers a startup of an environment -
StopInstance:
POST /api/v1/instance/{instance-id}/stoptriggers a shutdown of a single instance -
StartInstance:
POST /api/v1/instance/{instance-id}/starttriggers a startup of a single instance -
Refresh:
POST /api/v1/refreshforces backend to refresh it's cache -
Version:
GET /api/v1/versionreturns backend version information -
Config:
GET /api/v1/configreturns relevant backend configuration
It may be useful to mock the aws API when doing development work against the API (like for web ui development).
This means you don't need an aws api key. To enable this feature, set env variable POWER_TOGGLE_MOCK_ENABLED=true:
# build then start
make all
POWER_TOGGLE_MOCK_ENABLED=true ./bin/aws-power-toggle -config testdata/sampleconfig/power-toggle-config.yaml
if you would like to add/remove/change any of the fake inventory, then modify this file:
backend/mockdata.go
Certain features in the project are experimental and subject to further enhancements. Current experimental features include:
- Display billing stats: This feature displays the estimated total cost of all instances in each env. Counter will reset upon application restarts
To enable experimental features:
# set env variable POWER_TOGGLE_EXPERIMENTAL_ENABLED to true (or change experimental.enabled in config file):
export POWER_TOGGLE_EXPERIMENTAL_ENABLED=true