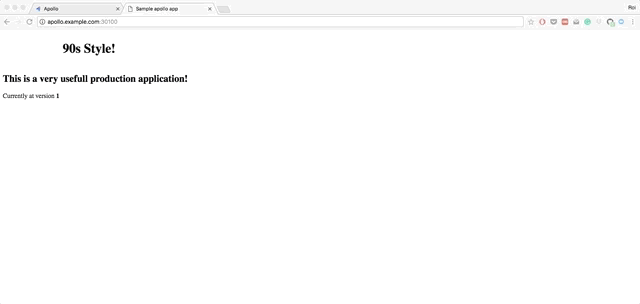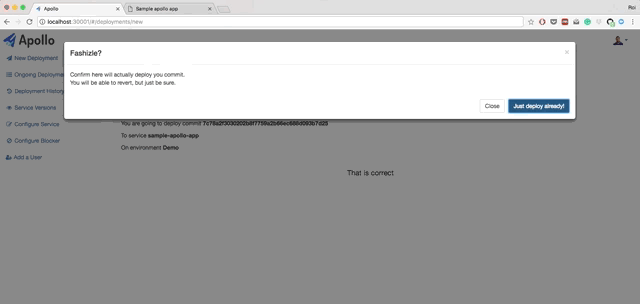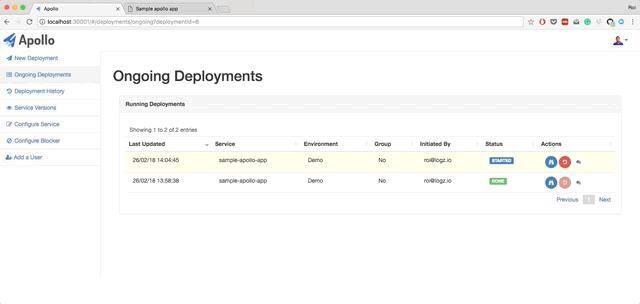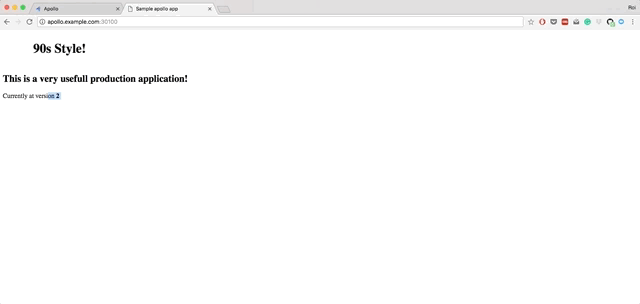
Apollo is a simple, lightweight, Continuous Deployment (CD) solution on top of Kubernetes. Apollo can integrate with any existing building process you might have in place. All you need to do is notify it of a ready artifact, and that's it.
Apollo also provides restricted access on top of Kubernetes. Each user has fine-grained permissions, to ensure safe deployments.
Please refer to the Wiki for more extensive documentation.
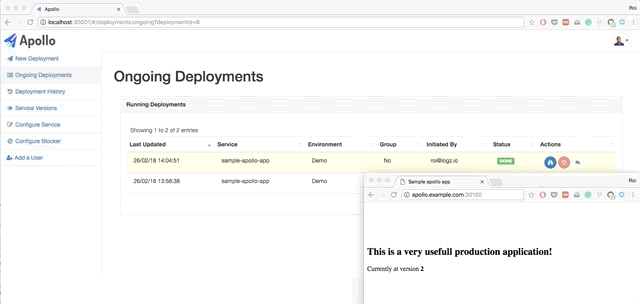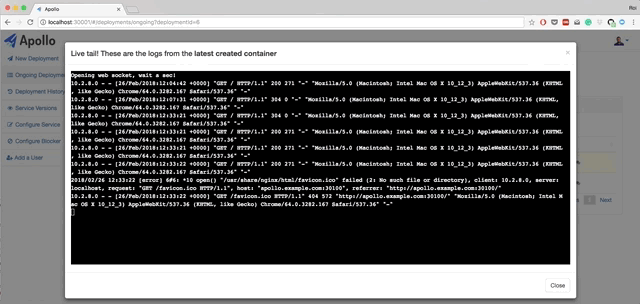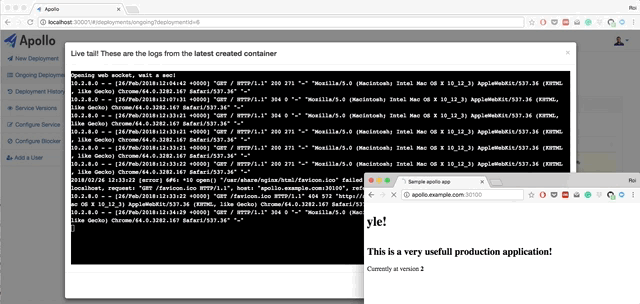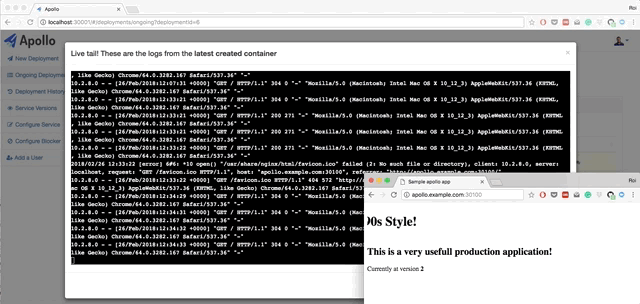
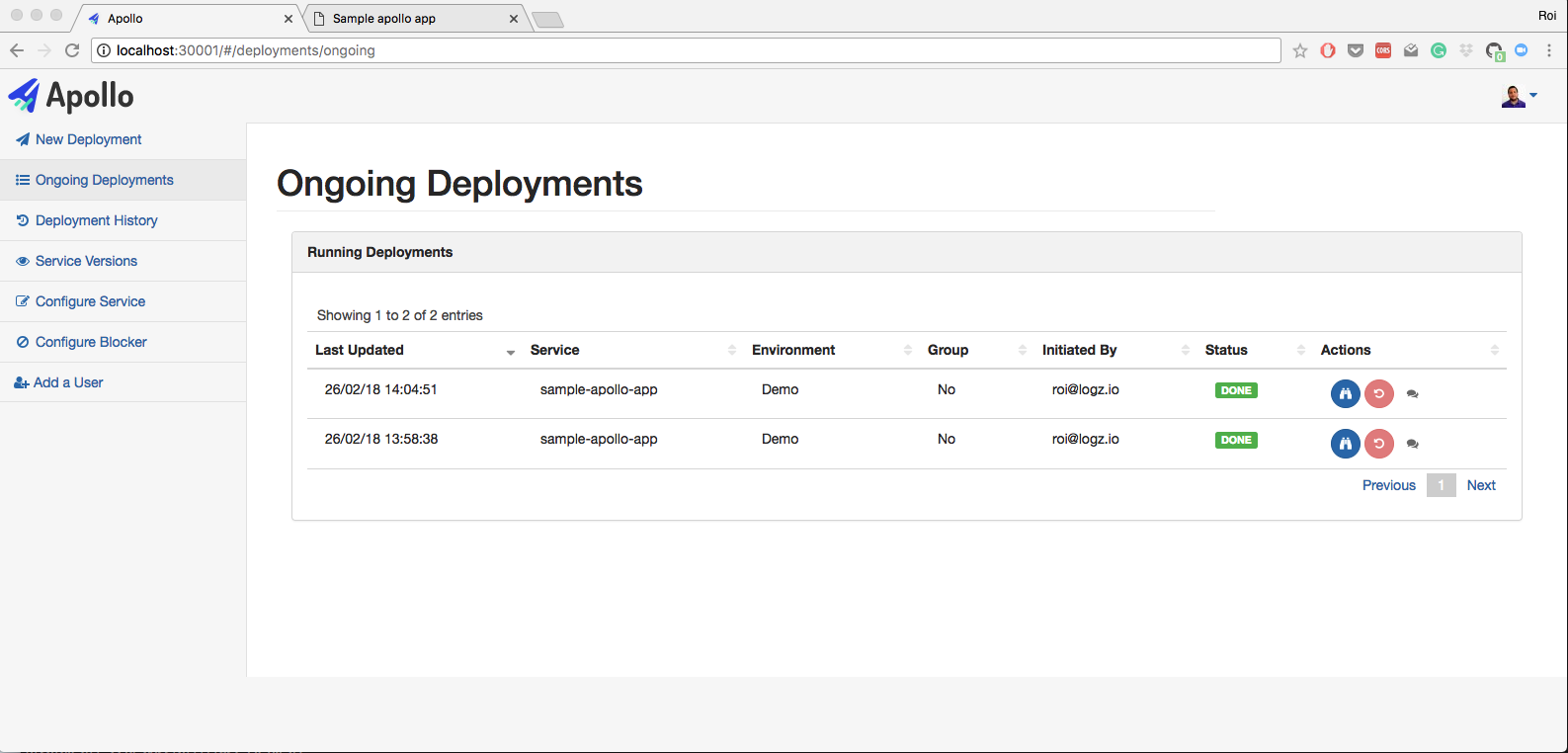
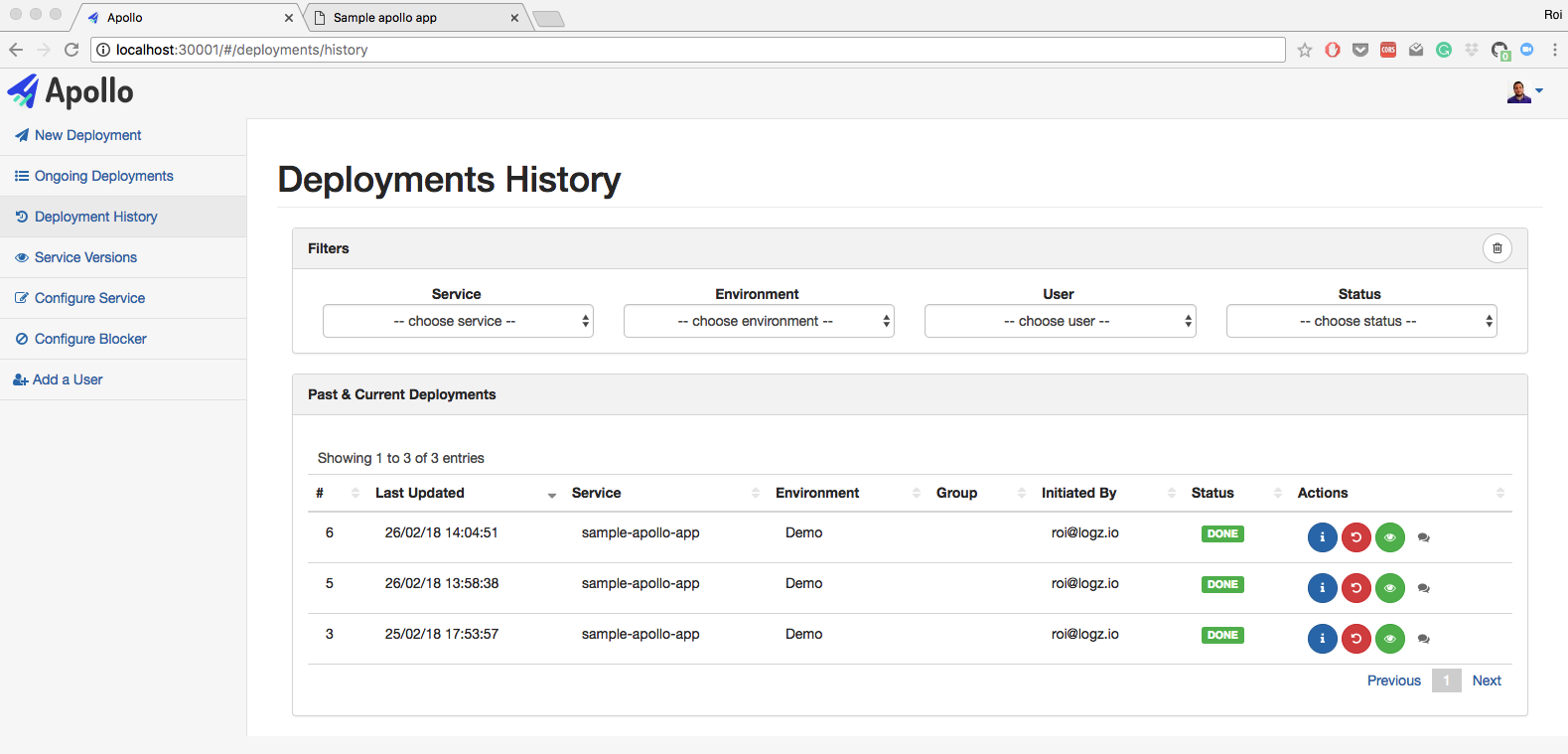
- Deploy a combination of a Kubernetes deployments and services into a designated Kubernetes cluster and namespace.
- View logs, revert deployments and get back to any point in time with just one click.
- Manage multiple Kubernetes clusters and multiple namespaces in the same cluster.
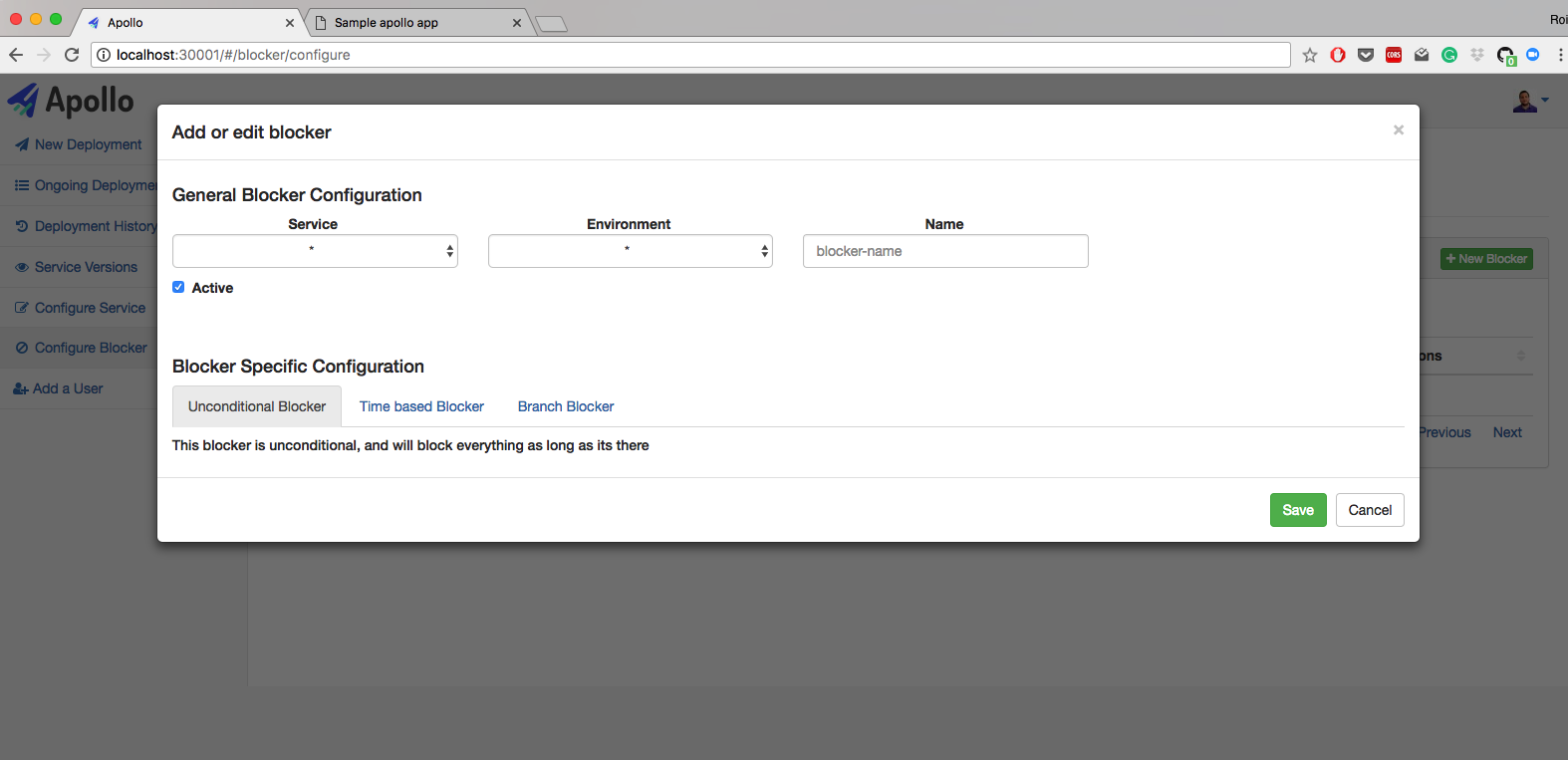
- Full permissions model for deployments. Each user can deploy only what he needs to deploy.
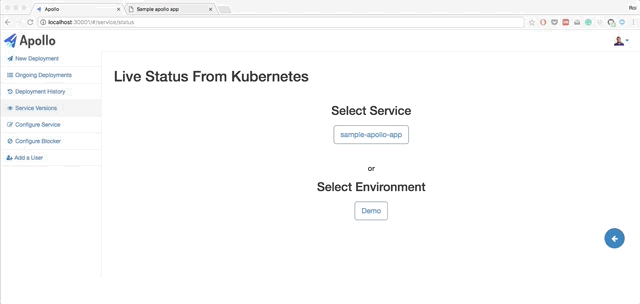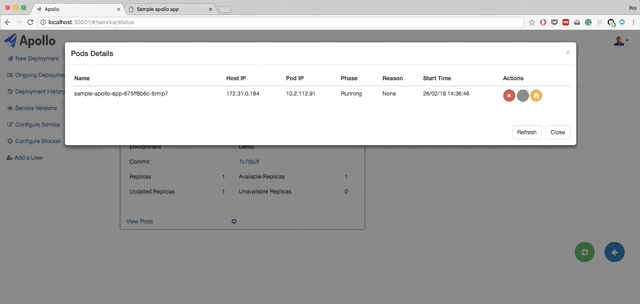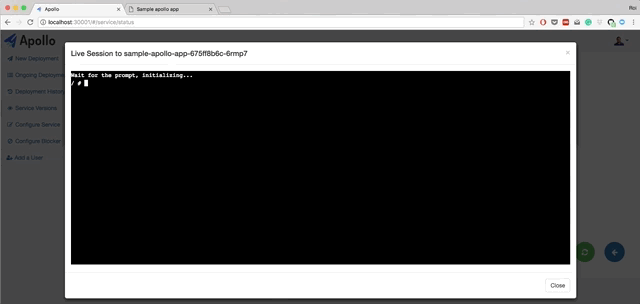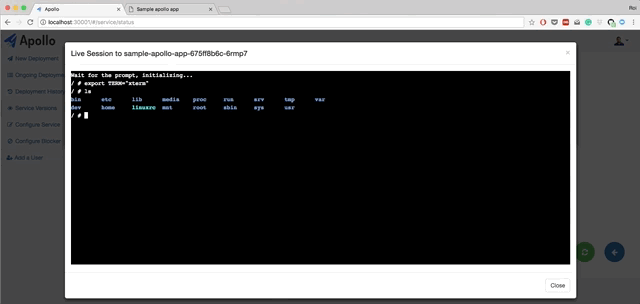
- Live querying on Kubernetes to get the current status of the deployments. You can also view pods status, view logs from each pod, and restart each pod.
- Full RESTful API and Java client to automate whatever you need, or deploy automatically.
- Once initially deployed, you can deploy future versions of Apollo, using Apollo!
Apollo requires a HOCON format configuration file to get all of its resources. Configurations can be supplied as a Filesystem path or as a Consul Key.
Configuration example:
apollo {
db { # Self explanatory
port = 3306
host = "..."
user = "apollo"
password = "..."
schema = "apollo"
}
api {
listen = "0.0.0.0" # Where should apollo backend listen
port = 8081 # And on which port
secret = "SuperTestingSecret" # Secret to encrypt websessions with
}
kubernetes {
monitoringFrequencySeconds = 5 # How frequent should the apollo's kubernetes monitoring thread check the deployment statuses
}
scm {
githubLogin = "" # Github user (in case you need private repositories access)
githubOauthToken = "" # Access token created in your user settings. Should have view access for private repos
}
}Under examples you can find a simple Docker Compose to help you set it up locally
cd examples/
docker-compose up -dFork away, commit, and send a pull request.