-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 52
MongoDB
The Logback MongoDB extension enables Logback to post messages to MongoDB, a scalable, high-performance, open source NoSQL database.
To use logback-access with Tomcat and MongoDB, place the files logback-core-1.0.6.jar, logback-access-1.0.6.jar, logback-ext-mongodb-core-0.1.0.jar, logback-ext-mongodb-access-0.1.0.jar and mongo-java-driver-2.7.3.jar under $TOMCAT_HOME/lib/ directory, where $TOMCAT_HOME is the folder where you have installed Tomcat. Please see also original logback-access configuration instructions.
To configure Tomcat in order to use LogbackValve, add the following lines to the Tomcat server configuration file, namely $TOMCAT_HOME/conf/server.xml:
<Valve className="ch.qos.logback.access.tomcat.LogbackValve"/>
and create a new file, namely $TOMCAT_HOME/conf/logback-access.xml with following content
<configuration>
<appender name="MONGO" class="ch.qos.logback.ext.mongodb.MongoDBAccessEventAppender">
<uri>mongodb://test:test@localhost/local.logs</uri>
</appender>
<appender-ref ref="MONGO" />
</configuration>
Start MongoDB daemon
mongod --dbpath /database/location
add the user test with password test to MongoDB database local and restart MongoDB daemon
mongod --auth --dbpath /database/location
with authentication enabled.
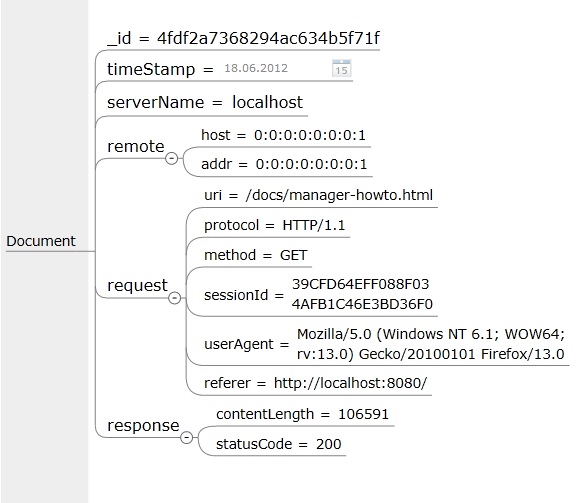
Start Tomcat and access via Browser a deployed web application. Your access logs are available in MongoDB:
mongo localhost/local -u test -p test
db.logs.count()
db.logs.find( {"response.statusCode": 200 } )
The structure of access logs looks like