-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
JVM Architecture
A Virtual Machine is a software implementation of a physical machine. Java was developed with the concept of WORA (Write Once Run Anywhere), which runs on a VM. The compiler compiles the Java file into a Java .class file, then that .class file is input into the JVM, which Loads and executes the class file. Below is a diagram of the Architecture of the JVM.
JVM is divided into three main subsystems: *** Class Loader Subsystem** *** Runtime Data Area** *** Execution Engine**
Java's dynamic class loading functionality is handled by the class loader subsystem. It loads, links. and initializes the class file when it refers to a class for the first time at runtime, not compile time.
1.1 Loading The Class loader reads the .class file, generate the corresponding binary data and save it in method area. For each .class file, JVM stores following information in method area.
- Fully qualified name of the loaded class and its immediate parent class.
- Whether .class file is related to Class or Interface or Enum
- Modifier, Variables and Method information etc.
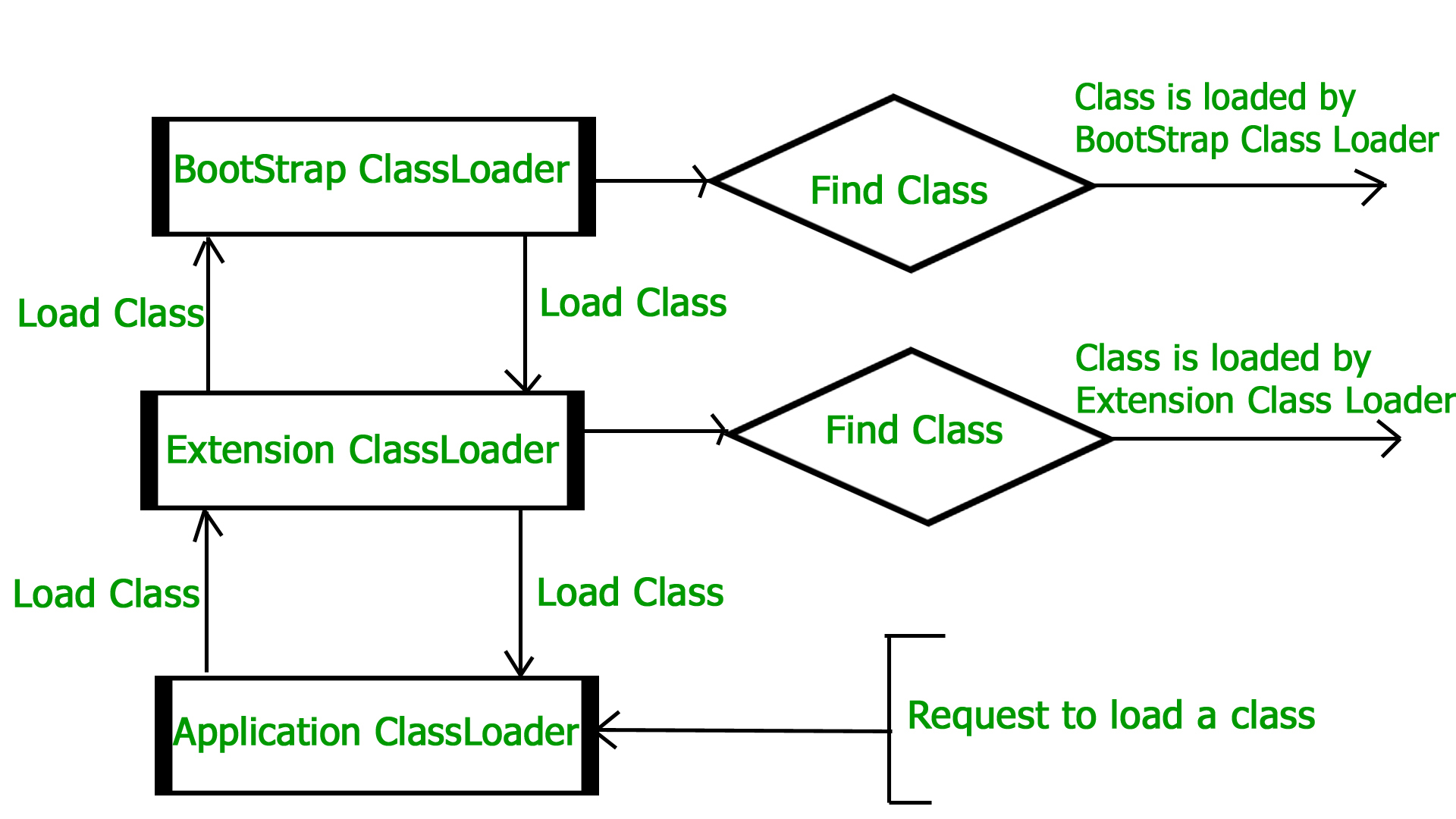
In general there are three class loaders : After loading .class file, JVM creates an object of type Class to represent this file in the heap memory. Please note that this object is of type Class predefined in java.lang package. This Class object can be used by the programmer for getting class level information like name of class, parent name, methods and variable information etc. To get this object reference we can use getClass() method of Object class.
Boot Strap ClassLoader – Responsible for loading classes from the bootstrap classpath, nothing but rt.jar. Highest priority will be given to this loader.
Extension ClassLoader – Responsible for loading classes which are inside ext folder (jre\lib).
System/Application ClassLoader –Responsible for loading Application Level Classpath, path mentioned Environment Variable etc. he above Class Loaders will follow **Delegation Hierarchy Algorithm **while loading the class files.
1.2 Linking Performs verification, preparation, and (optionally) resolution.
- Verification : It ensures the correctness of .class file i.e. it check whether this file is properly formatted and generated by valid compiler or not. If verification fails, we get run-time exception java.lang.VerifyError.
- Preparation : JVM allocates memory for class variables and initializing the memory to default values.
- Resolution : It is the process of replacing symbolic references from the type with direct references. It is done by searching into method area to locate the referenced entity.
**1.3 Initialization ** In this phase, all static variables are assigned with their values defined in the code and static block(if any). This is executed executed from top to bottom in a class and from parent to child in class hierarchy.
Note : JVM follow Delegation-Hierarchy principle to load classes. System class loader delegate load request to extension class loader and extension class loader delegate request to boot-strap class loader. If class found in boot-strap path, class is loaded otherwise request again transfers to extension class loader and then to system class loader. At last if system class loader fails to load class, then we get run-time exception java.lang.ClassNotFoundException.